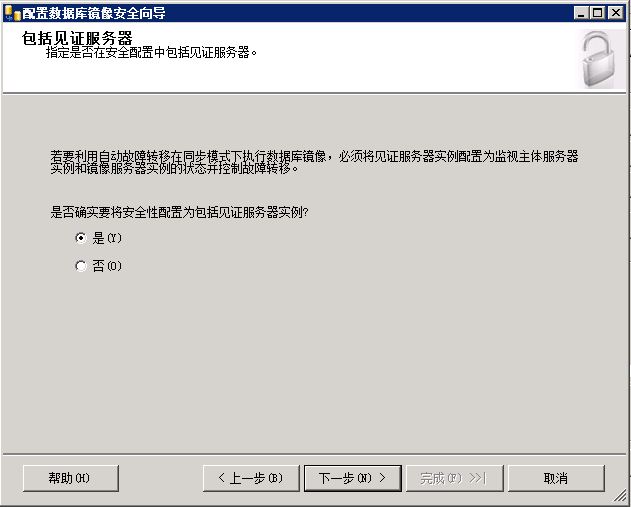
2013111220341541.jpg
悠久资源 2013111220341541.jpg https://www.u-9.cn/2013111220341541-jpg


常见问题
相关文章
猜你喜欢
- iQOO TWS 2怎么样 iQOO TWS 2体验评测 2024-04-19
- 2.4G闪连半入耳tws 才200+? 漫步者GT2S蓝牙2.4G双模耳机开箱测评 2024-04-19
- JBL TOUR PRO2怎么样 JBL蓝牙耳机TOUR PRO2体验评测 2024-04-19
- OPPO蓝牙耳机Enco Free3如何体验 OPPO蓝牙耳机Enco Free3开箱体验 2024-04-19
- 天猫精灵卡顿严重怎么解决? 天猫精灵变迟钝的解决办法 2024-04-19
- 华为GT-Runner智能手表怎么样 华为GT-Runner智能手表使用体验 2024-04-19
- 创米小白摄像机Y3尊享版怎么样 创米小白智能摄像机Y3尊享版开箱体验 2024-04-19
- 每月可免费作曲1000+首曲目!又一位AI作曲大师Udio加入混战! 2024-04-19
- 米兔儿童电话手表6X值得入手吗 米兔儿童电话手表6X开箱体验 2024-04-19
- JavaScript+PHP实现视频文件分片上传的示例代码 2024-04-19