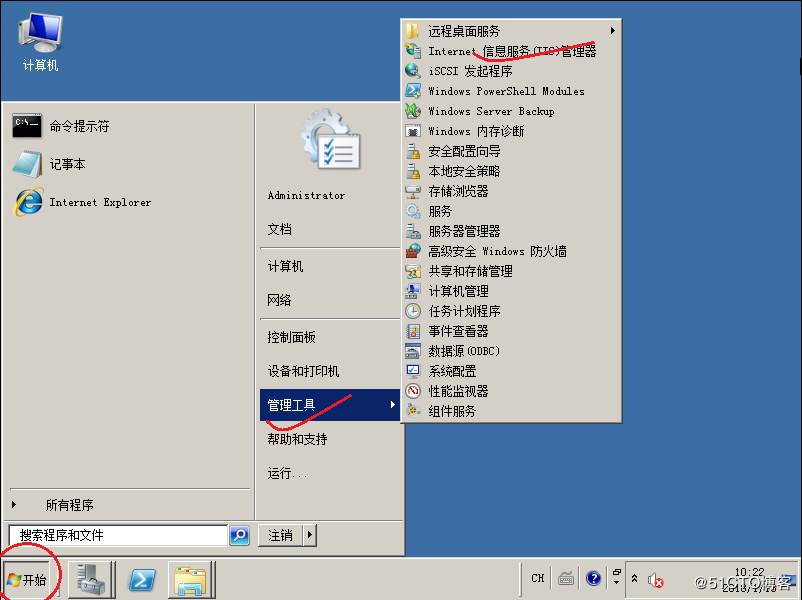
2020072409044419.png
悠久资源 2020072409044419.png https://www.u-9.cn/2020072409044419-png


常见问题
相关文章
猜你喜欢
- PConline × 希捷校园行丨到水木清华体验存储大厂技术魅力 2024-04-26
- AI绘画需要什么样的电脑配置?佰维这款NV7200 PCIe4.0 SSD给出了回答 2024-04-26
- 高性能办公娱乐迷你主机!磐镭HO4正式上市 2024-04-26
- 颜值与实力并存 OPPO K12:超级续航,十面耐摔 2024-04-26
- OPPO A3 Pro:耐用战神等你来选! 2024-04-26
- 99%女生都会喜欢的摄影搭子!佰维PD2000高速移动固态硬盘 2024-04-25
- 黑马杀出?奥日团队再创神作—《恶意不息》 2024-04-24
- AI强势赋能,存储体验升级,佰维PD2000高速移动固态硬盘 2024-04-24
- OPPOEncoAir2Pro吾皇猫定制版怎么样 真无线耳机EncoAir2Pro吾皇猫定制版详细评测 2024-04-24
- 99%女生都会喜欢的摄影搭子!佰维PD2000高速移动固态硬盘 2024-04-24